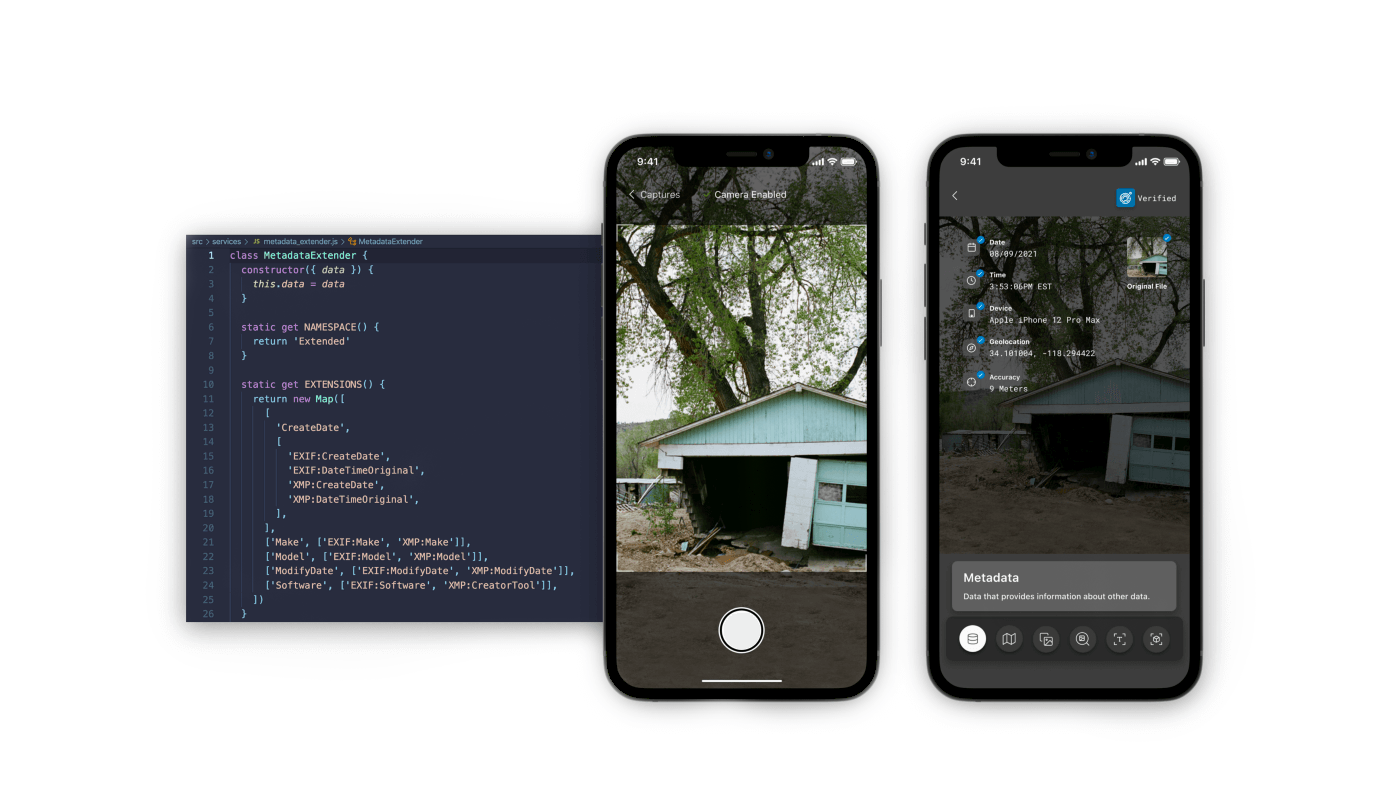
GLOSSARYCryptography
Cryptography is the practice of sending and receiving information in a way that is secure against malicious third parties.
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is the practice of sending and receiving information in a way that is secure against malicious third parties.
For example, if you send a confidential e-mail with sensitive information, you want to be sure that only the intended recipient can view that e-mail. Cryptography technologies allow you to communicate securely when in the presence of potential threats. But how does cryptography work?
There are two primary types of cryptography, symmetric and asymmetric.
Symmetric cryptography is the most commonly used form and can be thought of like this: the sender and recipient both have the same key that allows them to access information between them. When you send a message, it is encrypted. When the recipient receives your message, it is decrypted. However, if a third party were to intercept with the key, they will also be able to read the message.
Asymmetric cryptography, also called public-key cryptography, involves two different keys. A public key is sent out for everyone to encrypt the data and send a message, and then a second private key is used to decrypt the received message. Both keys are required to send and receive the message. This offers a higher level of security.
Cryptography aims to enhance confidentiality, data integrity and authentication, especially in a digital age where malware threats, scammers and digital content manipulation are on the rise.